installimage Script
The installimage script is an easy and fast method of installing various Linux distributions. You can run installimage directly from the client’s area on your server. Its menu interfaces make it easy to select the Linux distribution you want. You have full control over the how to partition your drive(s). And you can use a simple editor to define how you want to use software RAID and LVM.
Running installimage
To use installimage, you first need to activate the Rescue System and then boot into it Rescue System. Use the password displayed in the client’s area to log into the Rescue System as “root”. Then type installimage to start the installimage script: root@rescue ~ # installimage In the following menu, you should see:
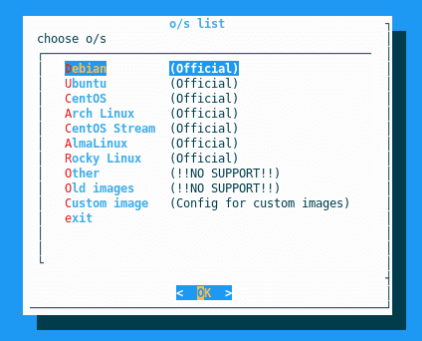
OS Choices
We offer a number of standard images that you can use. These are typically the latest versions of the particular distribution. Advanced users can also install older versions of these distributions, by going to the old_images folder. Important note: We don’t offer any support for these older images. In addition, advanced users can also create their own OS images and install them.
autosetup
If installimage finds an /autosetup file in the Rescue System, it will automatically use this as the configuration file. Unless there are errors in the files, you will not see a menu and or editor.
Variables
You can adjust the following variables to customize the installation.
Drives
The drives that are present in the server are identified in the first row with the variable DRIVE. Above each line, you can see the type of drive. Here, you can select which drives you want the OS to be installed on. The drives will be completely wiped, and all data currently on them will be lost. If you want to leave a drive in its current state and not make any changes to it, you can leave it out (remove it) by placing a # before it. Important note: Doing this means that you need to properly adjust the number after the next DRIVE variable. Example:
# SSDSC2BB480G4 #DRIVE1 /dev/sda # SSDSC2BB480G4 DRIVE1 /dev/sdbSWRAID
If the server has multiple drives, you can use the variables SWRAID and SWRAIDLEVEL to create different software RAID levels. Any software RAID levels are always applied to all drives. (That means drives marked with DRIVE, as discussed above.) drives. If you don’t want software RAID on a particular drive, you’ll need to remove it accordingly. The script can create software RAID with levels 0, 1, 5, 6 or 10.
Bootloader
The bootloader Grub is pre-configured. (In the past we also offered Lilo). Depending on the operating system, GRUB2 or GRUB1 (legacy Grub) is installed.
Hostname
The variable HOSTNAME sets the corresponding host name in the system.
Partitions / file systems
The installimage also supports adjustments to the partitioning scheme (including the use of LVM). You can find the designated syntax in the examples in the editor.
Operating system image
This is the full path to the operating system image; you only need to specify it if you are installing a custom image.
Installation
After leaving the editor with F10 (save and quit), the syntax of the config file is checked. Should it contain errors, you will be returned to the editor.
reboot in the Rescue System, root@rescue ~ # reboot the newly installed system is booted and you can log in with the previous Rescue System password.
Particularities
When installing Debian or Ubuntu using the installimage script, the times for the cronjob in /etc/cron.d/mdadm are set randomly.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why can’t I create partitions larger than 2 TiB?
You can create partitions larger than 2TiB only with a GUID partition table (GPT). Thus, you can only install operating systems which include GRUB2; it supports booting from GPT drives.
The installation script shows one or more errors. What should I do?
Re-run the installation. If you get the same error again, please send the complete screen output and the contents of the file /root/debug.txt by the ticket.
Do I have to put “all” at the end of the partition table or can I put this line further at the top?
The size all in the config file means use the rest of the available space on the drive. Since partitions are created one after another, the partition table will end after using all because there will be no space available afterwards. Of course, it is also possible not to use “all” at all.
Pressing F10 does not work. Instead ~21 (or something similar) is displayed.
Press ‘Escape’ and then 0. In most cases, this has the same effect as F10.
What is the MySQL Root password when LAMP has been installed?
You can find the MySQL root password on a LAMP image in the /password.txt file.









